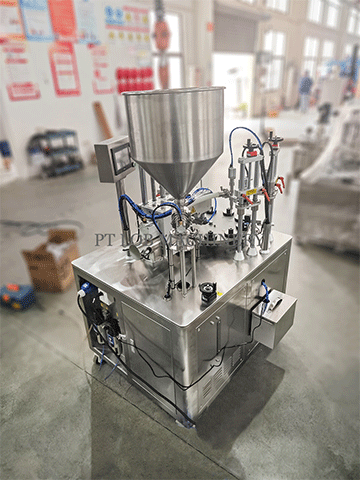
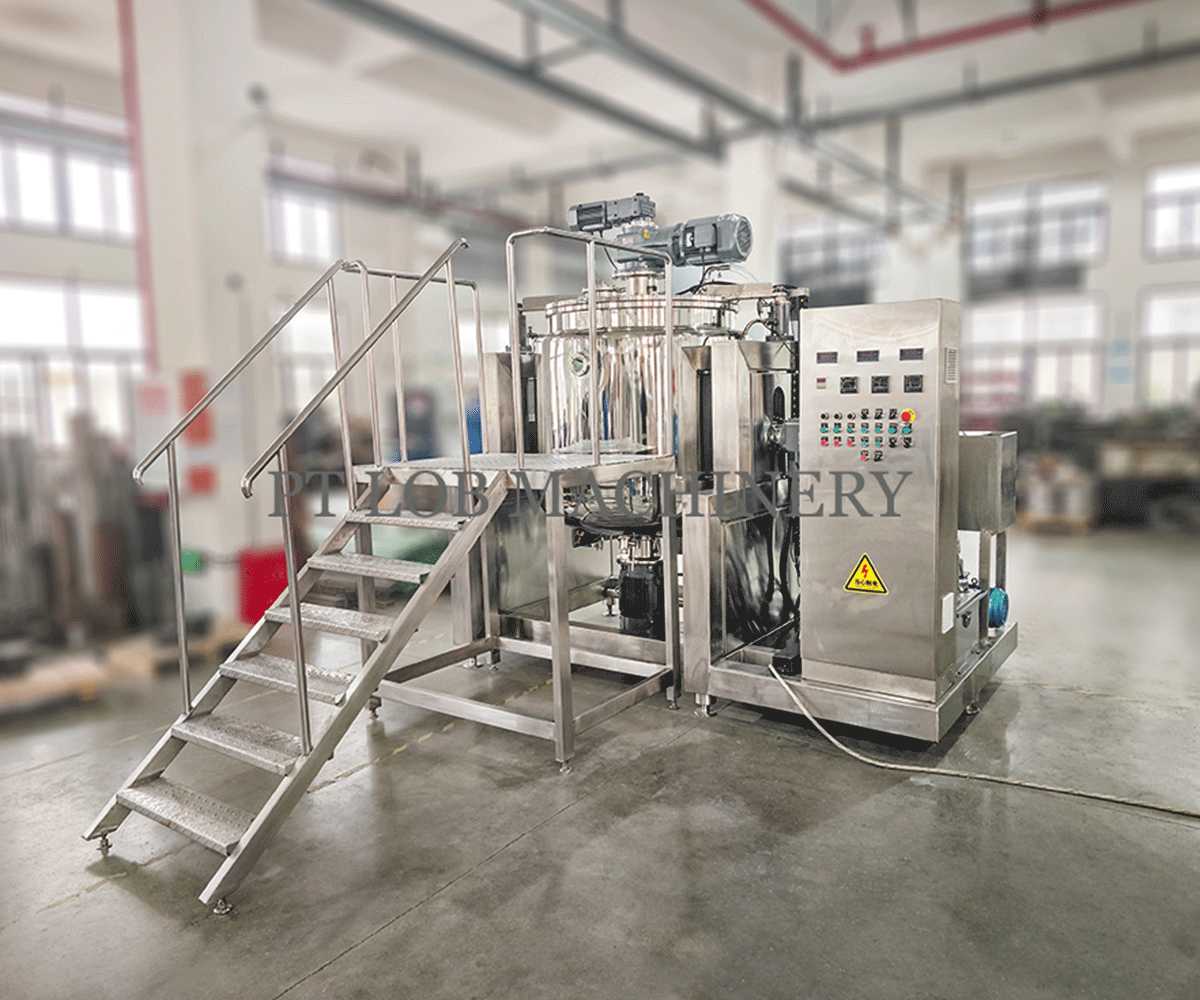
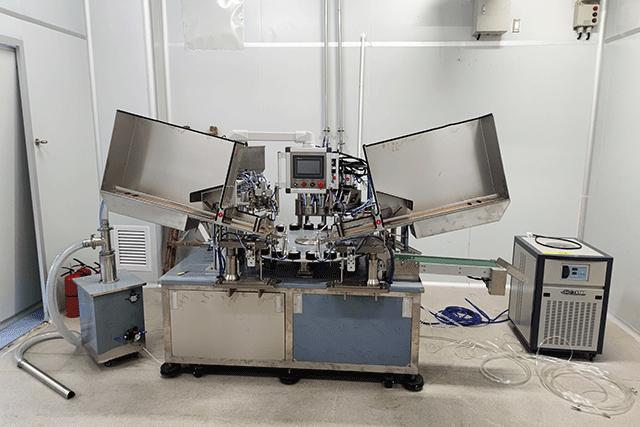
What is a Homogenizer
Introduction to Homogenizers
A homogenizer is a versatile and crucial piece of equipment used in a wide range of industries, from food and pharmaceuticals to cosmetics and biotechnology. Its primary function is to break down and mix particles or substances to create a uniform and consistent mixture. In this article, we will delve into the world of homogenizers, exploring their mechanisms, applications, and significance in various sectors.
The Mechanism of Homogenization
Homogenization is the process of reducing the size of particles or droplets within a mixture to achieve uniformity. A homogenizer accomplishes this through mechanical forces, typically involving high pressure and shear. The primary components of a homogenizer include a pump to generate pressure and a homogenizing valve or chamber where the product undergoes intense shearing. As the mixture passes through the valve or chamber, it experiences high turbulence, resulting in the breakdown of particles and their dispersion throughout the mixture.
Applications of Homogenizers
1. Food Industry
In the food industry, homogenizers are commonly used to ensure the consistency and quality of various products. They play a crucial role in dairy processing, as they break down fat globules in milk to create homogenized milk with a smoother texture. Additionally, they are employed in the production of salad dressings, sauces, and ice creams to prevent ingredient separation and enhance mouthfeel.
2. Pharmaceuticals
Homogenizers are essential in pharmaceuticals for various applications, including drug formulations and vaccine production. They help create stable emulsions, ensuring that active pharmaceutical ingredients are evenly distributed in formulations. This is vital for the efficacy and safety of pharmaceutical products.
3. Cosmetics and Personal Care
The cosmetics industry relies on homogenizers to create consistent and smooth products, such as lotions, creams, and makeup. Homogenization ensures that the ingredients blend seamlessly, providing a pleasant user experience.
4. Biotechnology
In biotechnology, homogenizers are used to break open cells, releasing cellular contents for analysis or processing. This is crucial for tasks like DNA extraction, protein purification, and cell disruption.
Advantages of Using Homogenizers
Homogenizers offer several advantages across industries:
-
Improved Product Quality: They enhance product consistency and quality by preventing phase separation and ensuring even distribution of components.
-
Increased Shelf Life: Homogenization can lead to better stability and longer shelf life for products.
-
Enhanced Bioavailability: In pharmaceuticals, homogenization can improve the bioavailability of drugs by reducing particle size.
Conclusion
In summary, a homogenizer is a vital tool with diverse applications in industries ranging from food and pharmaceuticals to cosmetics and biotechnology. Its ability to create uniform mixtures, improve product quality, and enhance bioavailability makes it an indispensable asset for numerous processes. Understanding the mechanisms and benefits of homogenization can help businesses make informed decisions regarding their use, ultimately contributing to better products and processes across various sectors.
 English
English